Overdubbing with a Samson\xc2\xae G-Track USB Microphone
| The procedure is similar for many other makes or models of USB microphones.
Hardware playthrough is not available when using a USB microphone that does not have a headphone output. |
Hardware
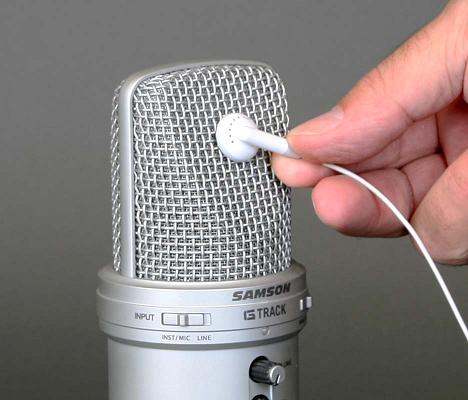
The Samson\xc2\xae G-Track is a good quality, large capsule, condenser USB microphone; it has a headphone connection in its base in addition to the USB connection.
The microphone has other tricks, but this tutorial will stick with a live acoustical performance. Leave the INST knob all the way down and pushed in.
Switch to INST/MIC and MONO and the microphone will mix sound from the computer playback with live performance sound. This is the mix you need to sing or play to yourself with no latency, echoes or other impairment.
Almost any Windows\xc2\xae, Mac\xc2\xae or Linux\xc2\xae machine with fast enough USB and good storage can be used.
Our example here uses Mac earbuds for listening, but nearly any good headphones or earbuds are OK.
If you require cranium-crushing headphone volume, you may need a headphone amplifier. You must get the headphone sound from the Samson G-Track, not from the computer soundcard.
Headphone monitoring is good; live microphones and speakers in the same room is a recipe for feedback.
The Samson G-Track has three jobs:
- It converts your voice or performance to digital and sends it down the USB cable for recording.
- It converts the USB digital audio from the computer back to analog.
- It has an internal headphone mixer. The G-Track can mix your existing track playback and your new, live performance so you can listen to both.
The one "magic" feature of this device is the ability to mix your live voice with the computer's rhythm track so you can hear the mixed musical performance and that can only happen if the rhythm track is available. Making the USB device the playback device makes this functionality available.
First Recording
First we will make a simple recording, with no overdubbing or other fancy tricks. The system has to work correctly for simple recording and playback before we go further.
Connect the USB and headphones.
The microphone must have a short, direct USB connection to the computer; USB audio will not go through a hub nor long USB extension cables.
|
This is not a tutorial on making a recording and playing it back, but you need to be able to do that before you do anything else. There are multiple tutorials and wikis on Recording.
Set the computer control panels, preferences and Audacity dropdowns to recognize the Samson G-Track USB device for both recording and playback. The G-Track's USB name is USB Audio CODEC
Set Audacity Preferences:
Click on (on a Mac this is )
- in the Quality tab:
- set Default Sample Rate to
- set Default Sample Format to
- in the Devices tab:
- Under Playback set Device to the microphone
- Under Recording set Device to the microphone and set Channels to .
- in the Recording tab:
- check
- uncheck
In Audacity by default using the Record button
|
Click once anywhere inside the recording meter (the one with the mic icon) to put the meters into Monitor Mode. They will display the microphone's sound level without sending Audacity into full record and wasting drive space. This may fail on certain Linux machines using Jack.
Switch the Samson G-Track to INST/MIC and MONO. The G-Track produces a half and half mix of computer playback and live performance. Set the VOLUME knob for comfortable listening.
Play or sing into the microphone. Adjust Audacity's recording control so you do not peak much over -10 to -6 on Audacity's meters. You can fix low levels later, but you cannot fix overloading, smashing, and clipping (meters too far to the right).
Click "Record"; Audacity will take a second to configure itself and start recording. The blue waves will start to crawl left to right as you perform. Play or sing a simple song that you can use for rhythm and timing tests later.
Click "Stop", then "Home" and then click "Play" to hear the track you have just made. You should hear the track in your headphones. This is all you will hear during the overdub sessions. You will only hear your voice or instrument in your headphones after you record it.
Setting the Recording Latency
Click "Home" then click "Record" and you will get a new recording underneath the first one. Sing or perform in time to the first track; when finished click on "Stop" then "Home".
The project will have two tracks, one from each performance, but it may be seriously out of time or rhythm -- even though you were in perfect time when you recorded it. This is recording latency and you can adjust it to zero using Audacity's latency tools; done properly, both the live recording session and the later playback will be in perfect time.
- Choose click "Don't Save".
- Choose .
- Choose click "OK" - to generate a click track
- Audacity set "Latency Correction" to [ 0 ] milliseconds, click "OK".
- Play the new track and set Audacity's volume to loud but not painful. Take off your earphones.
- Switch to CPU mode on the Samson G-Track.
- Turn the Samson G-Track MIC all the way up. Leave INST down and pushed in. It's not used.
- Push one of the headphones or earbuds against the G-Track grill:
- Click "Shift + Record". Track one's click track is now being recorded -- badly -- on track two through the headphone and microphone -- good fidelity here is irrelevant.
- Do this for five or ten seconds and click "Stop".
- Select the new track and choose (accepting the defaults) click "OK".
- Reduce Volume a bit and put your headphones back on.
- Click "Play", both tracks will probably play out of step.
- Magnify the Timeline around one of the pair of clicks (drag-select and CTRL+E - or on Mac CMD+E).
- Drag-Select the distance between the start of the click on the top track and the start of the same click on the bottom track.
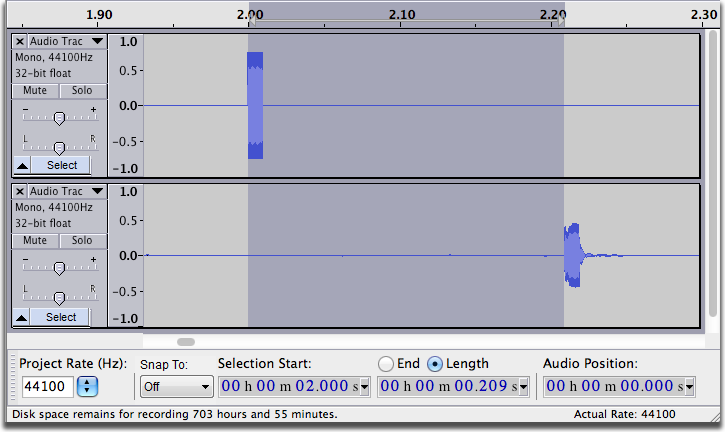
- That is how much the rhythm misses and that is the latency. Keep magnifying until you can get a good shot at accuracy. CTRL+3 - or on Mac CMD+3 to back out slightly if you magnify too much by accident.
- At the bottom of the Audacity window in the Selection Toolbar set the middle time control to "Length" (one of the two radio buttons) then change the format using the dropdown menu to:
- hh:mm:ss: + milliseconds
- hh:mm:ss: + milliseconds
- You are mostly interested in the milliseconds -- the last numbers on the right. The reading in the example above is 209 msec.
- Audacity set Latency Correction to the negative of the number in the Length display - in this case -209 milliseconds - then click "OK".
- Go through the whole process again.
- This time the two click tracks should look perfectly on (or very close to it) and sound perfectly in time. If not, zoom in, measure the new difference and add that number to the latency value.
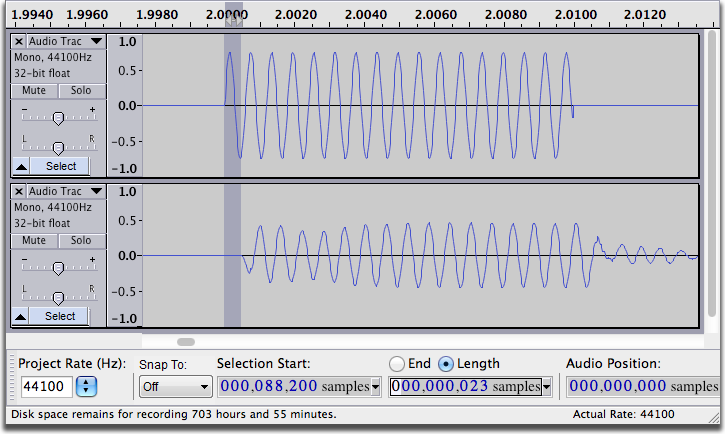
- In this example, the tracks align to within 23 samples, which is about 0.5 milliseconds - less than the smallest correction you can make in the Latency Correction. This is as good as it gets.
Performance
(you do not need to save any of your tests). You are ready for the first recording session.
Switch the Samson G-Track to INST/MIC and MONO, as it was for the first recording. Set the volume knob for comfortable listening.
Turn the G-Track MIC back to where it was for the first recording and switch to MONO.
The first recording can be whatever you are planning to use as a base, backing track, guide or rhythm track. It can be anything including or a rhythm and chord machine playing to the mixer.
You should record a lead-in. That is, a non-musical rhythmical clue before the music starts so as to warn you of the imminent start. In a live band, this would be the drummer or lead guitar count-in. You could use the keyboard rhythm stops or you can perform several rim shots into the microphone to establish the rhythm before the first note; tapping on the table with a pencil also works. You can sheer it off later in post production so nobody else will hear it. Tick, tick, tick, tick, music; adjust as appropriate for music type and rhythm.
Click "Stop", then "Home" and then "Shift + Record" to record track two using your live performance and track playback in your headphone mix as a guide. Repeat for as many tracks as required.
The or buttons to the left of each track are valuable in overdubbing. Solo causes only that track to play and Mute turns that track off. Solo has options that can be set in Tracks Behaviors Preferences. The little volume control to the left of each timeline also controls the playback volume -- it affects the headphone mix.
When you get to a stopping point click the Stop button ![]() then choose to save your project.
then choose to save your project.
As you progress, you should save a new Project periodically with a slightly different file name using .
A good recommendation is to use ISO date and time for the file names or the start of the file names; refrain from using slash marks or other punctuation marks in a file name.
201110011500.aup3 That is 3PM. 2011 October First, 1500hrs.
Then save a new version of the song about every twenty minutes:
201110011520.aup3
201110011545.aup3
Do not go weeks with one Project and file name, and never cover up or record over existing work. If anything happened to that one Project, your project would be ruined and could nullify weeks of work. Think of what would happen if the lights went out right now, the computer ground to a halt and you were forced to use the last known good version of the project.
For extra safety it is good practice to periodically back up your project versions to a DVD-R or external hard drive for archive purposes. In the unlikely event that the Audacity project is corrupted or your hard drive crashes you will be able to recover your work.
Note that Audacity projects cannot be played in computer media players nor burned to audio CDs. Export your project as 16-bit WAV or AIF for burning to a CD, or to MP3 for email or Internet delivery. See Mixing Audio Tracks, in the Audacity Manual, for advice on doing the final mix of your project.
Troubleshooting
|
- How much hard disk space do you have available? If your only experience with computer files is with spreadsheets, email or Photoshop pictures, live audio (and video) production will stun you with the amount of disk space it consumes. With high quality overdubbing and UNDO, project files and folders get big in a hurry; with periodic saving, a project can get very seriously large.
- Communications features on newer Windows machines can cause unwanted changes in recorded volume or make the recording sound tinkly and/or hollow. See this FAQ.
- Always ensure that you are directly connected to a USB port on your computer. You cannot send audio through a self-powered USB hub or share any hub, ever.
- USB microphones are lovely but have some interesting problems:
- You cannot get much further than about 10 feet (3 meters) from the computer.
- You cannot go through a self-powered USB hub or share any hub, ever.
- Generally, you can only connect one USB microphone directly to a computer, but see below.
Recording with more than one USB microphone
For information on how to record with multiple microphones please see FAQ:Recording - How To's#twomics this page in the Audacity Manual.



